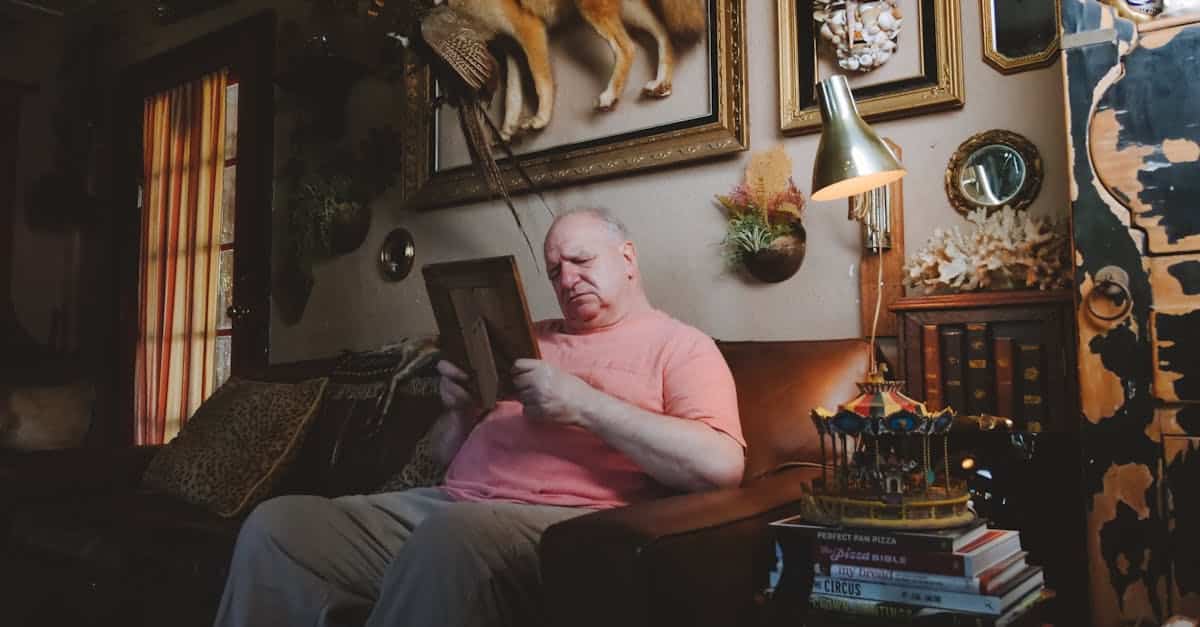
Dementia represents a set of major neurocognitive disorders, characterized by a deterioration of mental capacities. This complex pathology affects memory, reasoning, and behavior, inevitably leading to a loss of autonomy for those affected. Recognizing the different types of dementia and their symptoms is essential for better understanding this disease that impacts not only individuals but also their families and loved ones. The cognitive disorders associated with dementia pose daily challenges, but a better understanding can pave the way for innovative solutions to improve the quality of life for seniors.
Dementia is a generic term used to describe a set of symptoms that affect an individual’s cognition as well as behavior. These symptoms may include memory problems, reasoning difficulties, and the inability to perform daily tasks. Unlike occasional forgetfulness, dementia leads to significant and persistent degradation of mental functions.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), dementia is classified as a syndrome characterized by a global deterioration of cognition, often irreversible. It can affect various aspects of intellect, impacting memory, orientation, judgment, abstract thinking, as well as language abilities. This degradation can also lead to changes in behavior and emotions, thus affecting the social relationships of the person.
Among the common types of dementia, we find Alzheimer’s disease, which is the most widespread form. This neurodegenerative pathology usually occurs after the age of 65 and manifests as a gradual loss of cognitive functions. The early signs often include episodes of forgetfulness, followed by increasing difficulties in performing routine tasks.
Another type of dementia is Lewy body dementia, which manifests as fluctuations in attention and alertness, accompanied by parkinsonian symptoms and visual disturbances. This type of dementia is often misdiagnosed, as it shares characteristics with other cognitive disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Vascular dementia results from problems in blood flow to the brain, which can cause strokes and lead to cognitive deterioration. Symptoms may vary depending on the areas of the brain affected and can occur suddenly after a stroke.
The diagnosis of dementia is fundamentally clinical, relying on a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s mental state. Various tests and examinations may be conducted, but there is no unique method to diagnose this condition. Doctors therefore rely on clinical criteria, medical history, and functional assessments.
The consequences of dementia on daily life can be devastating. Cognitive disorders often impact the individual’s autonomy, making it difficult to manage everyday activities. Additionally, these disorders are often associated with emotional and behavioral issues, such as depression or anxiety, thus increasing the need for appropriate care.
It is particularly crucial to understand the issues related to managing dementia. Care must be personalized and tailored to the specific needs of each patient. Structures such as cantous, which are centers for natural activities, play a vital role in supporting people with dementia through meaningful and useful occupations.
Recent studies show that factors such as physical activity and even travel can influence the well-being and quality of life of seniors, including those with dementia. Furthermore, certain treatments, such as those related to menopause, may have a positive impact on the aging process, contributing to slowing the progression of the disease. To learn more, feel free to consult these articles: Travel and Aging, Menopause Treatments, and Understanding the Cantou.

FAQ: Definition of Dementia
What is dementia? Dementia is a syndrome characterized by a progressive loss of cognitive abilities, leading to a degradation of memory, reasoning, and behavior.
What are the main types of dementia? The main types of dementia include Alzheimer’s disease, Lewy body dementia, and frontotemporal dementia, each with unique characteristics.
How does Alzheimer’s disease manifest? Alzheimer’s disease often develops after the age of 65 and is characterized by an insidious cognitive deterioration that increasingly affects daily activities.
What are common symptoms of dementia? Symptoms include memory problems, communication difficulties, behavior changes, and orientation disorders.
How is dementia diagnosed? The diagnosis of dementia relies on a clinical evaluation, combined with cognitive tests and sometimes brain imaging examinations.
What is the difference between dementia and delirium? Dementia is a chronic and prolonged degradation of cognitive functions, while delirium is a short-term mental disturbance often caused by environmental or medical factors.
Can dementia be treated? Although there is no curative treatment, certain approaches can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Medications and behavioral therapies are often used.
What impacts does dementia have on daily life? Dementia can affect autonomy, requiring support in daily activities, as well as particular attention to the emotional and behavioral status of affected individuals.