The occupational therapist is a health professional whose role focuses on the assessment and rehabilitation of individuals with disabilities or loss of autonomy. Their intervention is based on a thorough analysis of the individual’s residual capabilities, whether physical, psychological, or social. Through adapted techniques, they work to restore lost functions and help their patients regain their independence and fully participate in their daily life activities.
Table des matières
ToggleGlossary: Definition of the Occupational Therapist and Their Role in Rehabilitation
The occupational therapist is a health professional specialized in improving the quality of life for individuals experiencing loss of autonomy or suffering from functional limitations. Their main mission is to evaluate and support individuals in order to help them regain their independence in daily activities. Occupational therapy relies on the fundamental link between human activity and health, making it a key player in the rehabilitation process.
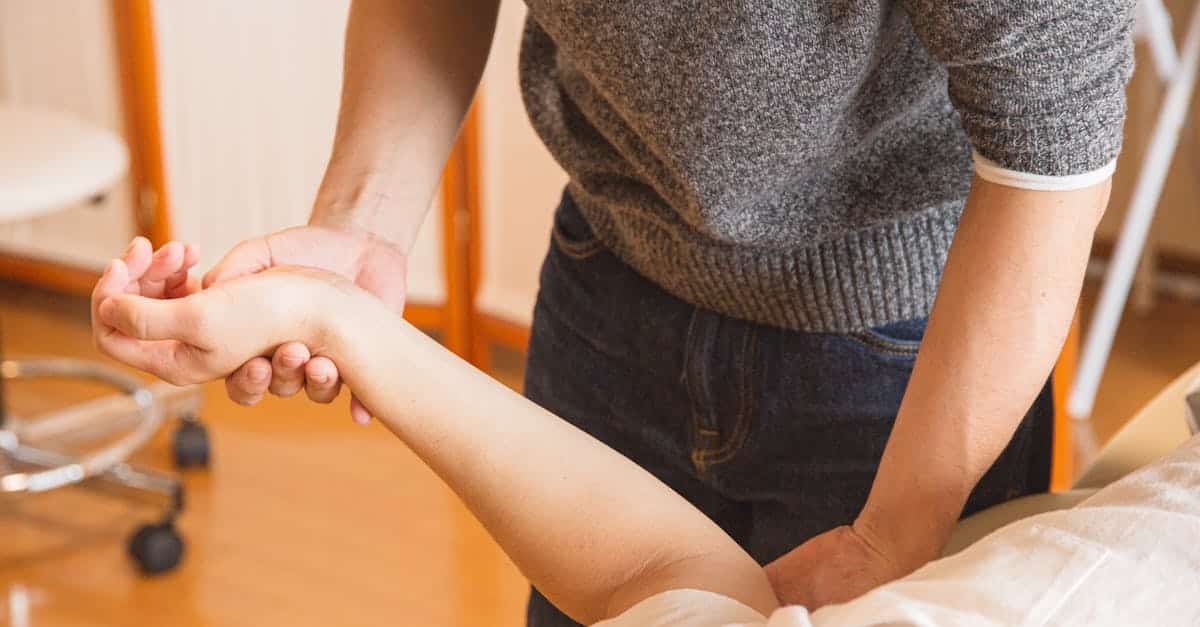
At the heart of the occupational therapist’s intervention is the assessment. During this crucial step, the professional analyzes the residual capabilities of the person. This analysis encompasses the evaluation of physical, psychological, and social aspects to create a complete profile of the patient’s situation. By understanding the specificities of each individual, the occupational therapist can develop a personalized intervention plan. The goal is to identify the individual’s strengths and limitations while considering their environment and lifestyle habits.
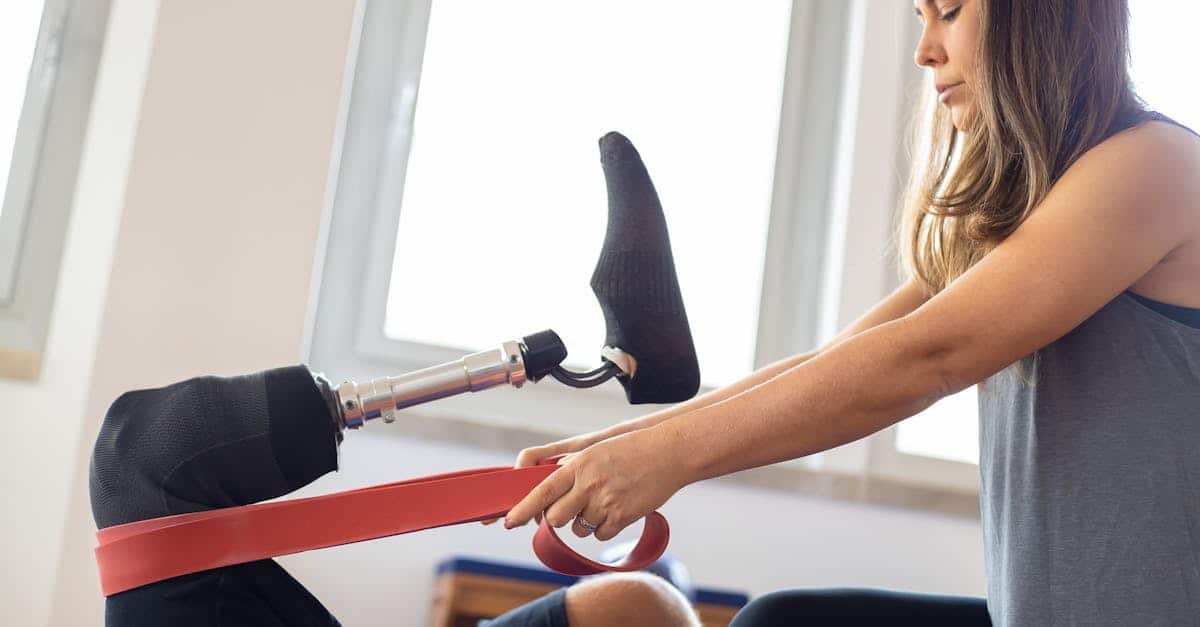
Once the assessment is completed, the occupational therapist proposes adapted interventions. These interventions may include the re-education and rehabilitation of lost or altered functions. The specialized techniques aim to assist patients in learning new ways to accomplish daily tasks, whether it’s simple actions like dressing, eating, or moving around. The occupational therapist thus plays an important role in the rehabilitation of elderly individuals, teaching them practical strategies to improve their autonomy.
An essential aspect of occupational therapy is the prevention of disability situations. By considering the needs of each individual and adapting their living environment, occupational therapists help reduce the risk of loss of autonomy. Their intervention may include advice on home modifications or the use of assistive devices. These modifications allow individuals to feel safe and perform their daily activities more effectively.
Occupational therapists work in various settings such as hospitals, clinics, rehabilitation centers, and home care facilities. Their clients range from young children to elderly individuals, each with unique needs and specific challenges. This professionalism is reflected in their holistic approach, which considers not only physical aspects but also the psychological and social dimensions that influence the patients’ quality of life.
In terms of rehabilitation, the occupational therapist often collaborates with other health professionals such as doctors, physiotherapists, and social workers. This teamwork ensures a comprehensive and coherent care process for patients, ensuring that no aspect of their rehabilitation is overlooked. The exchanges between these various practitioners are crucial to creating a care pathway tailored to each person.
Ultimately, the occupational therapist is much more than just an intervenor in the rehabilitation process. They are a champion of autonomy, a supporter who helps individuals overcome the challenges of daily life. Their role is essential in improving the quality of life for those with disabilities or loss of autonomy, providing them with tools to thrive within their family and social environment. For more strategies on improving daily mobility for the elderly, visit this site.